Cladding is a technology belonging to the group of high energy density treatment processes, melting added material on the piece. In laser-beam cladding, a high-energy laser beam fuses together a layer of the base surface and the added material, which may be several millimetres thick. A distinction is made between powder cladding and wire cladding. The large variety of materials that can be applied ensures a wide range of applications for the finished products coated in that way. The resulting coating enhances the physical and chemical properties of the finished product, e.g.: outstanding hardness (up to 63-65+ HRC), high corrosion resistance, long-term heat resistance, or extreme acid and alkali resistance.
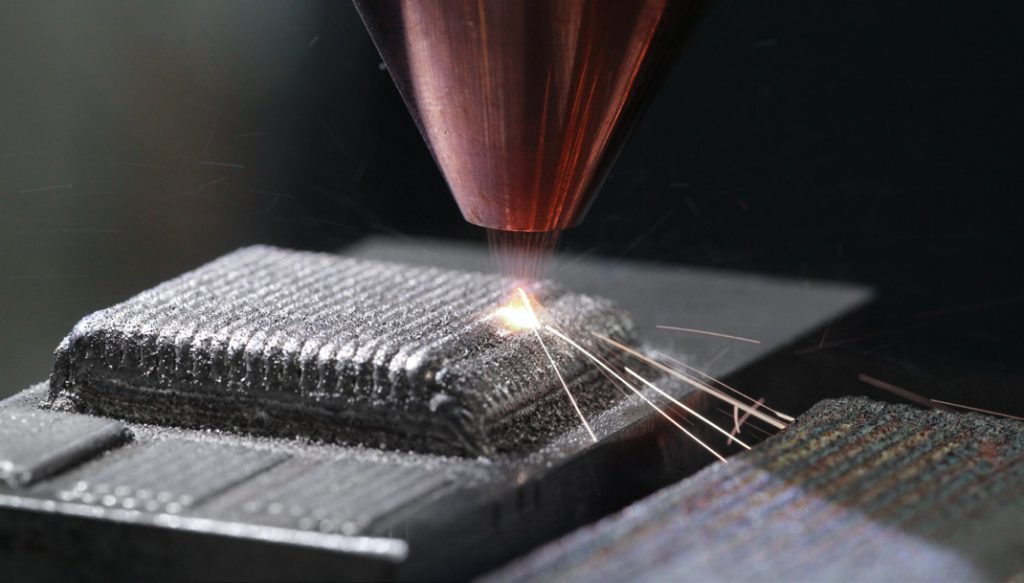
As a result of the process, a new layer with a material quality different from the base material is melted and coated on the surface. Thanks to this technology, it is sufficient to coat the surface of the treated part that is exposed to special use, while the base body can be made from a lower quality material, reducing the manufacturing costs. It is also excellent for repair purposes as a replacement for build-up welding, for the restoration of worn tools/components, and for improving their surface properties. Unlike conventional build-up welding, no inclusions are formed.
During cladding, a fused alloy zone is created between the base material and the surface layer. Due to the large mixing zone, the bond between the base material and the applied material layer is very strong and stable. The precise and quick power control of the high-energy laser light helps to create the desired homogeneous coating, which can be 1-6 mm thick in one layer. The coating thickness can be further increased by applying several layers on top of one another. The very fast cooling rate of the cladding process results in a coating with a fine, high-strength microstructure, with minimal effect on the mechanical properties of the base material.
Cutting tools
Coated saw blades, counter-blades, disc harrows and other cutting tools can be protected against wear and corrosion, while providing excellent cutting properties. These coated tools can be used in industry, including construction industry and agriculture.
Hydraulic cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders used in mining need to be coated to protect them against corrosion caused by the local atmosphere. In the past, chrome plating was primarily used, but it is increasingly being replaced by cladding, thanks to its outstanding durability. Some estimates suggest that cladding can improve the durability of these products by 100%.
Drilling tools
Heavy-duty drilling tools are used in several industries, including oil and gas industry and mining. The wear protection, resistance and service life of these tools can be increased so that they withstand the stresses they are exposed to.
Heat exchangers
Heat exchangers come into contact with corrosive liquids and gases. Coatings containing materials with good corrosion resistance and toughness, such as nickel alloys, prevent the cracking of heat exchangers and improve wear protection even at permanently high temperatures.
Ask for an individual offer!

A special service of our company, unique in Hungary and the surrounding countries, is that we can perform laser hardening and cladding at the customer's site.
2024 © APZ Laser Kft.
Dear Visitors!
Our company will be closed between 21 December 2024 and 6 January 2025.
Thank you for your understanding, we wish you happy holidays and a happy new year!